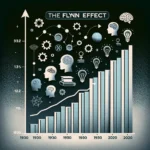
Fluid Intelligence: Understanding a Core Cognitive Ability **Definition of Fluid Intelligence** Fluid intelligence is a critical aspect of human cognition, pertaining to the capacity to reason, solve new problems, and adapt to novel situations without relying on prior knowledge and experience. Unlike crystallized intelligence, which is built through acquiring knowledge and skills, fluid intelligence is […]